Helsing to Deliver 6,000 AI-Powered Strike Drones to Ukraine
Image Source: Helsing
Helsing, a leading European defense technology company, has announced a significant expansion in its AI-driven drone manufacturing capabilities. The company is set to produce 6,000 HX-2 strike drones for Ukraine, following an earlier batch of 4,000 HF-1 drones currently being delivered.
[Read More: AI Warfare: Autonomous Weapons Changing the Battlefield]
The HX-2: AI-Powered, Electrically Propelled, and Swarm-Capable
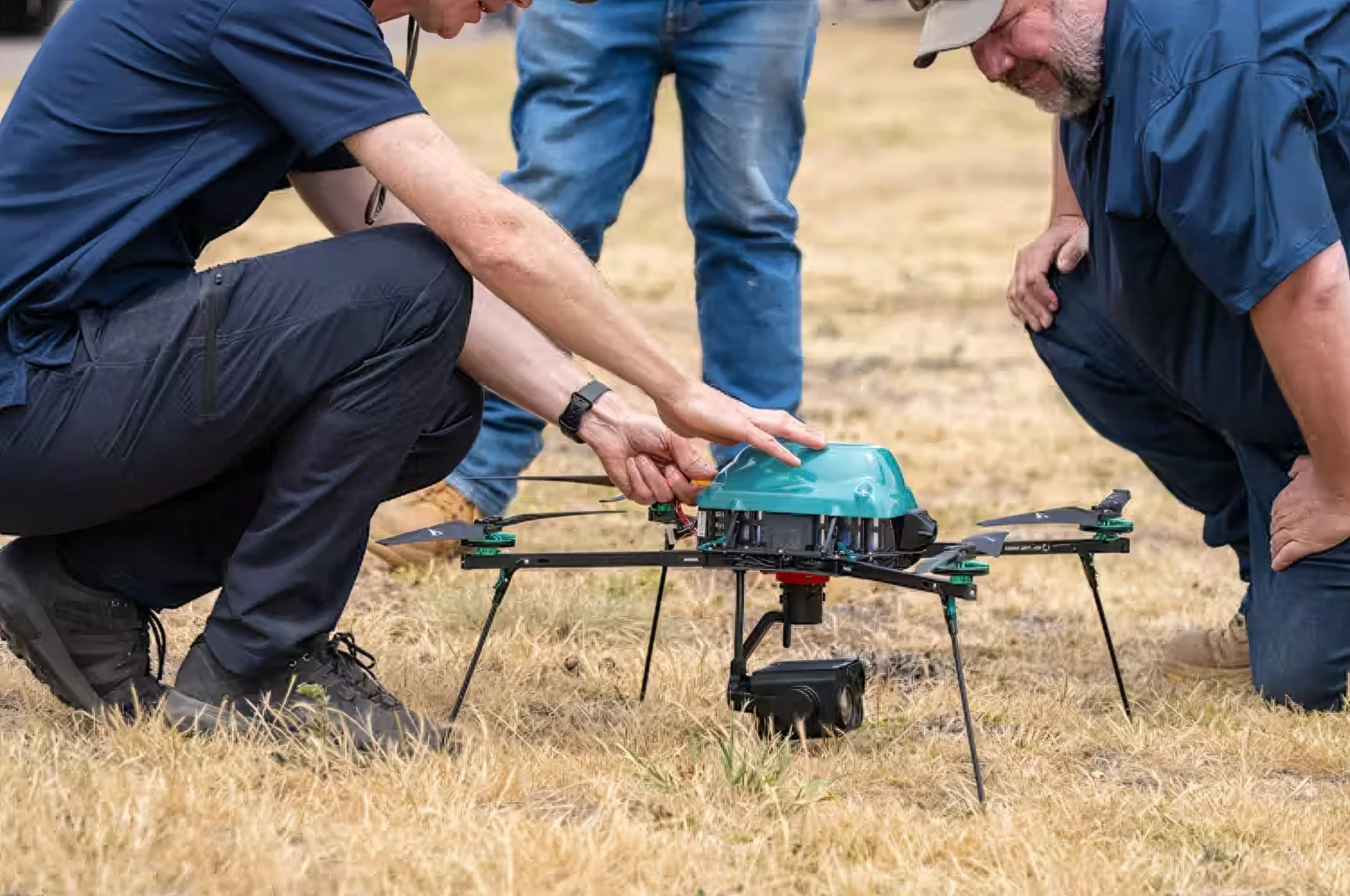
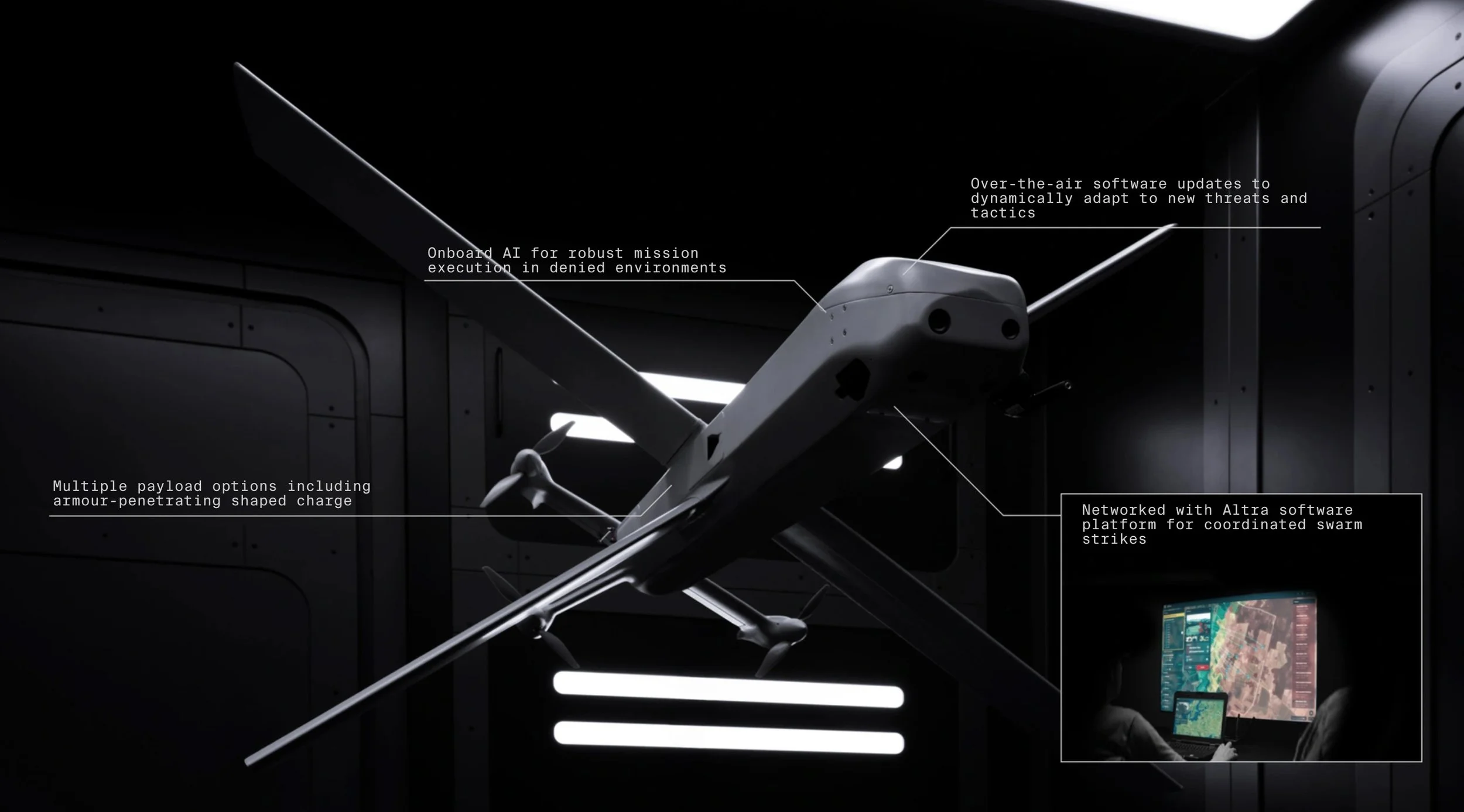
Introduced in late 2024, the HX-2 is an advanced X-wing precision munition featuring an electric propulsion system and an operational range of up to 100 km. Weighing 12 kg and capable of reaching a maximum speed of 220 km/h, HX-2 is designed to engage artillery, armored, and other military targets at beyond-line-of-sight range.
What sets the HX-2 apart is its AI-driven resistance to electronic warfare (EW), ensuring reliability even in contested environments. Onboard artificial intelligence enables HX-2 to search for, re-identify, and engage targets even without a signal or continuous data connection. A human operator remains in or on the loop for all critical decisions, ensuring oversight in its use.
Further enhancing its capabilities, the HX-2 integrates with Helsing’s Altra reconnaissance-strike software, allowing multiple units to operate as AI-coordinated swarms controlled by a single human operator. This marks a significant advancement in the use of AI for networked combat operations, reducing human workload while increasing effectiveness in targeting and adaptability on the battlefield.
Image Source: Helsing
Mass Production and the 'Resilience Factory' Model
To meet growing demand, Helsing has launched its first Resilience Factory (RF-1) in Southern Germany, capable of producing over 1,000 HX-2 drones per month. This facility represents a new model of distributed, high-efficiency production that aims to provide European nations with sovereign defense manufacturing capabilities.
Helsing’s long-term strategy involves expanding Resilience Factories across Europe to ensure rapid scalability in times of conflict. This model not only enhances local defense autonomy but also reduces reliance on external suppliers, which has been a critical vulnerability in recent geopolitical conflicts.
[Read More: Thales Unveils AI-Driven Drone Swarms: Enhanced Autonomy & Mission Flexibility]
Image Source: Helsing
The Role of AI in Overcoming Warfare Challenges
Helsing's AI-first approach focuses on solving critical battlefield challenges, such as mitigating electronic jamming, optimizing swarm dynamics, and improving cost efficiency. Unlike traditional weapons that rely on expensive hardware improvements, Helsing embeds AI-driven adaptability into its software, allowing for continuous enhancements without redesigning physical components.
The AI capabilities of the HX-2 offer multiple advantages:
Electronic Warfare Resilience: AI-powered signal processing enables drones to navigate and strike even in GPS-denied environments.
Swarm Intelligence: Multiple drones communicate and adapt in real-time, optimizing attack strategies.
Cost Efficiency: Mass-producible design reduces unit costs, making precision warfare more accessible to allied nations.
Image Source: Helsing
Strategic Implications for NATO and Modern Warfare
Helsing’s expansion signals a broader trend in military AI development, where autonomous and semi-autonomous systems are increasingly shaping the battlefield. The lessons from Ukraine’s defense strategies—leveraging AI-powered precision over numerical advantage—highlight a potential shift in NATO’s approach to modern warfare.
Co-founder Gundbert Scherf emphasized the strategic necessity of AI-driven mass precision, noting that “precision mass is offsetting a numerical disadvantage in legacy systems”. His counterpart, Niklas Köhler, reinforced this, stating that Helsing’s software-first design approach prioritizes affordability and effectiveness, ensuring long-term deterrence.
[Read More: AI Arms Race: Navigating the Tumultuous Waters of Global Tech Dominance]
Ethical Responsibility and AI Governance
Helsing places a strong emphasis on ethics in defense technology development, recognizing that the integration of AI into warfare necessitates responsible decision-making. The company asserts that protecting open, democratic societies is a collective responsibility, and that advanced technologies like artificial intelligence must be developed with careful ethical considerations.
The company has established quantitative and qualitative guidelines for evaluating potential customer nations, ensuring that their technology is deployed responsibly. Helsing’s internal ethics processes are designed to be transparent and standardized, offering accountability in decision-making both at the time of deployment and historically.
Additionally, Helsing actively studies the effectiveness of human oversight in AI-driven warfare, considering factors such as cognitive load, perceived AI reliability, fatigue, and UX design. The company acknowledges that ethical AI implementation requires constant refinement and engagement with public debate and international guidelines.
Helsing also fosters a culture of ethical scrutiny within the organization, ensuring that employee discussions and workshops contribute to refining their ethical standards. According to Helsing, maintaining control over ethical trade-offs in AI warfare is a responsibility that democratic societies cannot afford to outsource.
[Read More: AI Can Handle 100 Drones at a Time!]
Security Concerns of AI-Enabled Lethal Systems
Despite Helsing’s emphasis on ethics, AI-driven warfare still raises serious concerns about autonomy in lethal decision-making. The debate over human-in-the-loop versus human-on-the-loop control mechanisms remains unresolved, particularly as AI-driven drones become more independent in target selection and execution.
One of the most pressing concerns is whether future AI-enabled drones could operate autonomously without human intervention, leading to the risk of unintended attacks or collateral damage. If AI systems gain the capability to select and engage targets independently, the risk of misidentification, mission drift, or even rogue behavior becomes a serious ethical and security challenge. Could AI drones mistakenly target civilians or non-combatants? Could adversaries hack or manipulate these autonomous systems to turn them against their intended operators? These questions highlight the urgent need for strict governance, safeguards, and accountability frameworks.
Additionally, the proliferation of AI-powered precision weapons could escalate arms races, making such technology accessible to adversaries in unforeseen ways. The risk of AI-powered autonomous warfare without clear international regulations could destabilize geopolitical landscapes and lead to unintended conflicts.
To prevent these scenarios, robust security measures, human oversight mechanisms, and international agreements will be necessary. Ensuring that AI-driven lethal systems remain under strict human control and are programmed with fail-safe mechanisms will be crucial in mitigating these risks.
Source: Helsing