AI in Firefighting: How Smart Tech is Enhancing Wildfire Detection and Response
Image Credit: Australian National University
In the face of escalating wildfire threats exacerbated by climate change, the integration of Artificial Intelligence into firefighting strategies has become a focal point for enhancing detection, prediction, and response.
[Read More: United by AI: 20 Drones Join Forces to Battle Wildfires]
Historical Context: The Genesis of AI in Firefighting
The journey of AI in firefighting began with the need to process vast datasets to predict fire behaviour and optimize resource allocation. Early implementations focused on developing algorithms capable of analyzing historical fire data, weather patterns, and vegetation maps to forecast potential fire outbreaks. These foundational efforts laid the groundwork for more sophisticated AI applications in the field.
[Read More: Google's FireSat: Harnessing AI Satellites to Combat Australia's Bushfire Crisis]
Current AI Applications in Firefighting
1. Early Detection Systems
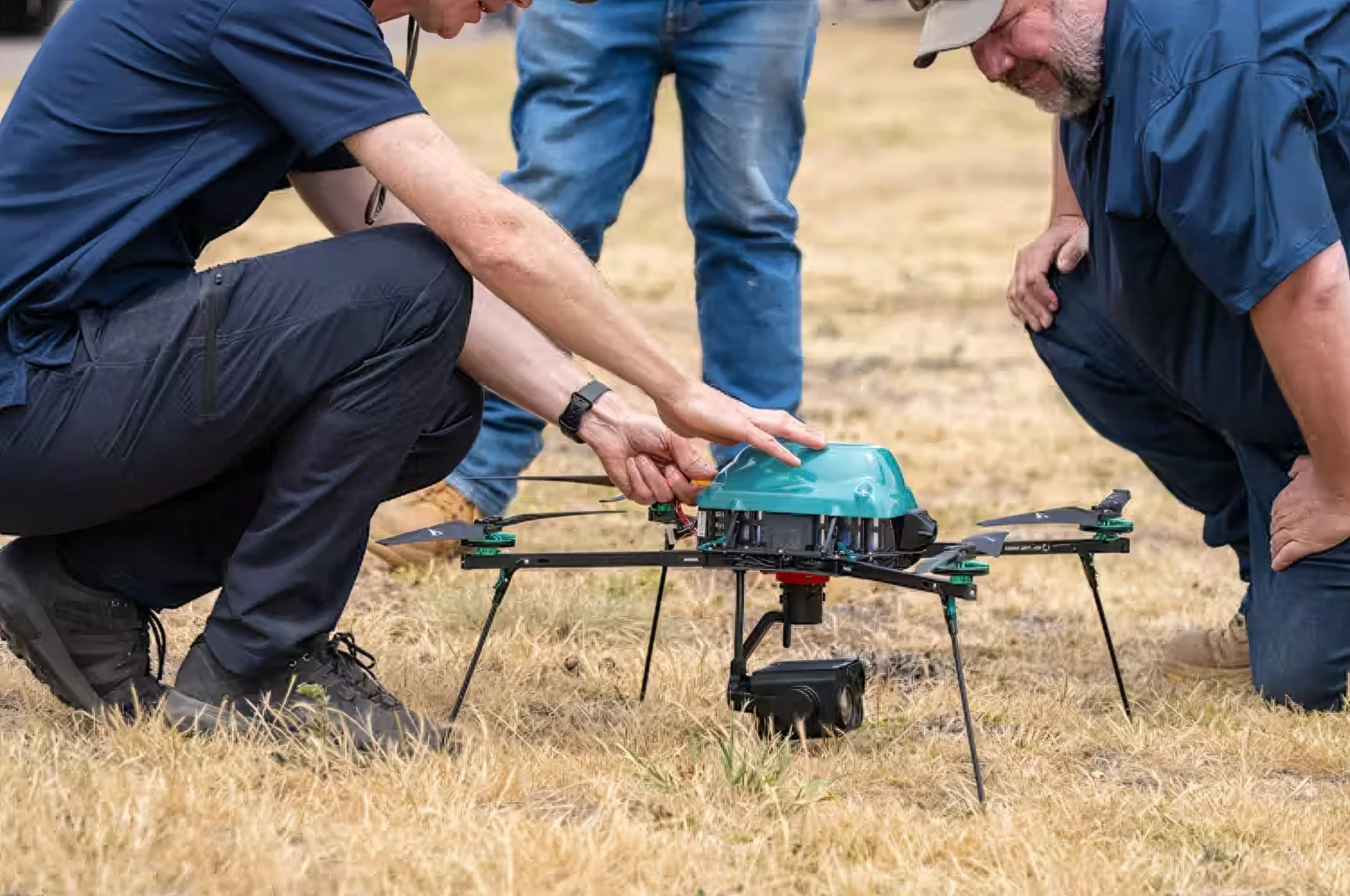
AI-Powered Cameras: The Victorian Government, in collaboration with the Australian Government, has invested AU$1.5 million each into a Remote Sensing Bushfire Detection project since October 2024. This project assesses the reliability of AI software using ground-based cameras mounted on fire lookouts across the state to detect smoke and provide GPS coordinates of potential fires, thereby enabling rapid response. The project is being conducted by Forest Fire Management Victoria (FFMVic), the state's lead agency for managing bushfire risk on public land. The trial's first phase occurred during the 2023-24 fire season, with cameras installed at locations including Mt Gordon, Mt Wombat, and Peters Hill. The second phase is scheduled for the 2024-2025 fire season, with plans to expand camera installations to additional sites.
AI-Powered Bushfire Detection: Companies like exci and Pano AI have developed advanced AI-driven bushfire detection systems. Exci's system uses real-time images from ground-based cameras to monitor smoke, complementing the efforts of Fire Lookout Observers and providing continuous 24/7 monitoring. Similarly, Pano AI offers a comprehensive solution that integrates ultra-high-definition 360-degree panoramic cameras, satellite feeds, artificial intelligence, and modern cloud software to detect and pinpoint new ignitions, alerting fire professionals within minutes.
Satellite Monitoring: Researchers from the University of South Australia (UniSA), funded by the SmartSat Cooperative Research Centre (CRC), have developed an AI-enabled early fire smoke detection system for South Australia's first cube satellite, Kanyini. This system processes hyperspectral imagery directly onboard the satellite, allowing for the detection of bushfires from space 500 times faster than traditional ground-based methods. The AI model reduces the volume of data downlinked to 16% of its original size while consuming 69% less energy compared to traditional on-ground processing. In a case study of a past fire event in the Coorong region, the simulated Kanyini AI onboard approach detected smoke and transmitted the data to the South Pole ground station in less than 14 minutes.
[Read More: AI-Powered Analysis Reveals Accelerated Glacier Retreat in Svalbard]
2. Predictive Analytics
Athena Program: The New South Wales Rural Fire Service (NSWRFS) has implemented the Athena, which is an advanced bushfire intelligence system developed in collaboration with the Australian technology company Kablamo. It integrates artificial intelligence to analyze data from various sources, including mapping, weather reports, satellites, and live feeds. One of Athena's notable features is its Social Intelligence Dashboard, which monitors social media platforms to detect unreported fires and gather real-time information on fire behaviour. This capability enhances situational awareness and supports rapid response efforts. Since its deployment, Athena has tracked over 15,000 fire incidents, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing bushfire management and response strategies.
Firestory™ Platform: Developed by the Australian technology company Kablamo, Firestory™ is a cloud-based data and artificial intelligence platform designed for bushfire management, prediction, and prevention. It consolidates extensive bushfire-related data into a single source of actionable intelligence, aiding in strategic planning and resource deployment. Firestory™ has been recognized for its innovative approach to bushfire management. The platform was awarded the 2021 AWS Global Public Sector Partners Award for Most Innovative AI and ML Solution and received the Best Tech Innovation award at the 2021 Finder Innovation Awards.
3. Unmanned Aerial Systems and Drones
Scout Drones: The ANU-Optus Bushfire Research Centre of Excellence, in collaboration with the ACT Rural Fire Service and drone manufacturer Carbonix, is advancing drone technology to provide early validation of lightning-induced bushfire ignitions. These drones are equipped with thermal cameras and sensors capable of detecting small spot fires from significant distances, even under dense forest canopies. They can pinpoint fire locations and map affected areas, delivering critical real-time information to ground crews. Notably, these drones are designed to operate beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) and in adverse conditions, such as at night or during inclement weather, where traditional piloted aircraft may face limitations.
Water Gliders: Australian National University (ANU) is developing autonomous, GPS-guided water gliders designed to deliver water or fire retardant to suppress bushfires in their early stages. These gliders are intended to be deployed from aircraft flying at high altitudes, allowing for rapid response to detected ignitions. By releasing water gliders from higher altitudes, the approach aims to enhance safety and enable quick suppression of small fires, even during nighttime or adverse weather conditions when traditional aerial firefighting methods may be limited.
[Read More: NASA Enhances Disaster Response Capabilities with Advanced Technology]
Global Perspectives and Future Directions
Internationally, AI's role in firefighting is expanding. Operated by the University of California, San Diego, ALERTCalifornia utilizes a network of over 1,000 AI-powered cameras to monitor high-risk wildfire areas. In 2024, this system detected 77 wildfires before any 911 calls were made, enabling rapid response and potentially preventing larger conflagrations. Recognized as one of the best inventions of 2023 by TIME magazine, ALERTCalifornia’s AI-driven detection system has been hailed as an innovative contribution to public safety.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI with robotics holds great promise. Experts anticipate that AI-powered robots will play a crucial role in combating wildfires, particularly in hazardous environments.
In January 2025, Jim Fan, Senior Research Manager at NVIDIA, discussed the role of AI-powered robots in firefighting. He emphasized that these robots can operate in dangerous conditions and carry heavy loads, making them ideal for disaster recovery efforts. While acknowledging that the technology is still maturing, Fan noted that rapid advancements in AI suggest the widespread adoption of such robots is imminent.
Designed to function in environments unsafe for human firefighters, these robots can carry heavy loads and perform tasks such as clearing firebreaks and delivering fire retardants. For instance, the KT-500 robot is specifically engineered to assist in wildfire control by swiftly masticating undergrowth to create firebreaks.
[Read More: Canberra Earthquake Highlights Need for AI in Seismic Detection]
Source: Forest Fire Management Victoria, HAD, EXCI, Pano.ai, UNISA, Kablamo, AFAC, CA GOV, Robot Report, Barron’s